The origin and history of oriental sweets
July 17, 2023
What are bread improvers? .. And what are its components?
July 18, 2023What is the maintenance of the equipment?
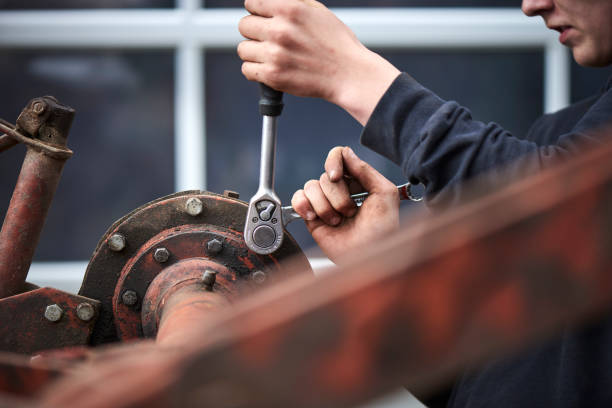
Equipment maintenance is any process used to keep a company’s equipment in good working order. Equipment may include mechanical assets, tools, heavy vehicles, computer systems, and more. The resources needed to keep it all in good condition vary by species. For example, it won’t Repairs to heavy construction equipment are similar to those to food processing machinery. Let’s get to know the importance and goals of equipment maintenance.
Types of maintenance
You should know the types of maintenance you encounter as a business owner or manager, i.e. proactive maintenance strategies and responsive maintenance strategies. Within these groups, we’ll cover several specific types of maintenance, including preventive, predictive, planned, condition-based, reactive, emergency, and corrective maintenance. We will talk more about what these different types of maintenance entail, what they cost, and how they will contribute to the long-term success of your business.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is defined as taking steps or precautionary measures to prevent equipment failures before they occur. Preventive maintenance usually includes routine checks, upgrades, modifications, and replacement of obsolete equipment or parts
Advantages of preventive maintenance
First: Reducing downtime and business closures due to unexpected equipment failures – this will help you avoid financial loss and protect your profits
Second : increase the life expectancy of equipment and essential assets – Inspecting, updating, and caring for your business assets will result in you spending less money on new equipment in the long run.
Third : lower energy consumption for your business assets – when equipment is operating optimally, less energy is required, which means lower costs

Planned maintenance
Planned maintenance covers any maintenance that is planned, scheduled and documented, basically planned maintenance is performed to reduce business downtime, which often stems from unexpected equipment malfunction and can significantly affect the bottom line of the business. In the event of such a failure, any plan or strategy that would get the equipment involved up and running again would be a type of planned maintenance.
Preventive maintenance is one type of planned maintenance, and it will take into account machine malfunctions and prevent them before they happen. There is also planned and unscheduled maintenance, which is the process of correcting or repairing an already broken system, and anticipating these business blockages ahead of time. For example (if you run a fleet of cars, having spare batteries on hand so replacing a broken battery is quick and easy)

Interactive maintenance
Reactive maintenance is any response or reaction to fixing a broken machine that needs repair. It focuses on returning damaged equipment to normal operating conditions, (if applicable). This process usually requires the services of a mechanic, or assistance from the manufacturer or supplier, to repair the broken machine

Emergency maintenance
Emergency maintenance is a type of maintenance that is required when an asset experiences an unexpected malfunction that could cause significant health and safety problems or significant production delays. The problem must be addressed as soon as possible, hence the emergency maintenance
But the main challenge is that a “quick fix” is seldom as simple as it seems. There are often major breakdowns that require coordination among all members of staff. As such emergency repairs pose major operational problems for maintenance managers

Stages of the maintenance process
First: Define the problem The need for maintenance can be caused by a malfunction, oil leak, or other fault. Once a problem is identified, it must be reported to the maintenance department. This is usually done through a work order so that planning and scheduling can take place
Second: Planning the maintenance process Planning involves deciding what exactly needs to be done, setting priority, and determining the sequence of activities and skills required. Ensure that all resources, materials, labour, contract services, specialized equipment, tools and information are available
The maintenance planning function is an important tool for minimizing downtime and maximizing the value of preventative maintenance. Therefore the maintenance planner must possess the technical skills and knowledge of the equipment to carry out this planning
Third: work scheduling involves deciding when to do the work. This will depend on the priority level of the task, the availability of both resources and the equipment to be repaired. Many organizations schedule maintenance for a set period during the business week or month. Weekend maintenance is never desirable because, in many cases, technicians are not available at that time
Fourth: Assigning the task to specific people Allocate maintenance personnel and ensure that the assigned person has the necessary skills to perform the task Be very clear about the type of work to be assigned to external technicians when necessary Perform hazard analyzes to identify risks and formulate action plans to control access to high risk areas
Fifth: Ensure that the work is carried out correctly It is usually the responsibility of the maintenance supervisor to ensure that maintenance work meets the required quality standards, usually through planned and selected job observations (or in some cases post-maintenance monitoring) to ensure that the planned work is actually done
Sixth: Solving the problem and how to prevent it from happening again It is important to analyze the root cause of failure and take corrective action to prevent recurrence. Corrective actions can include training, a change in the preventive maintenance program, or a change in the way equipment is used. The breakdown or failure of the management process is often overlooked in the event of a major failure. In these cases, corrective action may be a systems upgrade.
Why should you care about maintenance?
There is no doubt that taking care of the maintenance of your equipment is one of the basic and necessary matters in the field of the food industry, and it has many benefits, let us get to know them
* Preserving the safety of workers by reducing the risk of injuries and thus avoiding problems that may appear and hinder the production process
* Prevent costly downtime events that can disrupt production and lead to loss
* Extending the useful life of assets and increasing their resale value at the end of their useful life
* Reducing future maintenance costs that may occur suddenly
* Increasing the efficiency of the equipment and thus continuing productivity and increasing the profit margin
* Reduce energy consumption and operating costs.